How to Read a Json From File and Put It in Mysql Java
How to Read JSON Data and Insert it into a Database
GoAnywhere MFT tin connect to RESTful web services for transferring or manipulating JSON and other data formats. Learn more nigh JSON and RESTful Spider web Services.
In this tutorial, you lot will acquire how to utilize GoAnywhere Managed File Transfer to read data from JSON files and load that data into RowSet variables using the Read JSON chore. Those RowSets can and then be used to insert the information into a database or translate the data to another file type such as XML, Excel, fixed-width, or CSV with no coding required.
Not using GoAnywhere MFT yet? Get-go a complimentary trial and examination it out for 30 days.
Outset Free TRIAL
JSON
JSON is short for JavaScript Object Annotation. JSON is represented in a logical, organized, and easy-to-access manner. JSON files can comprise multiple levels of objects, arrays, and various field data that can exist parsed by GoAnywhere MFT. When GoAnywhere reads a JSON file, the contents of the file are stored in one or more RowSet variables, which incorporate a listing of records. For example, you could have a JSON file that contains customer information forth with a list of the products the customer ordered. The customer information can exist parsed into ane RowSet and the list of products into another RowSet. Those RowSet variables tin then be inserted into two split database tables or written to another format, like CSV, Excel, or XML.
The following image represents a simple JSON input file and will be referred to throughout this tutorial:

Create a New Project
To begin, create a new Project following the Getting Started with Projects tutorial.
Project Designer – The Read JSON Job
From within the Projection Designer folio, aggrandize the Information Translation folder in the Component Library, and then drag the Read JSON task to the Project Outline.

On the Read JSON task, specify values for the File attribute:
- Input File – The file path and file name of the JSON file to read.
- Input File Sets – Optionally, you tin can define a File Set that contains a list of files to read.
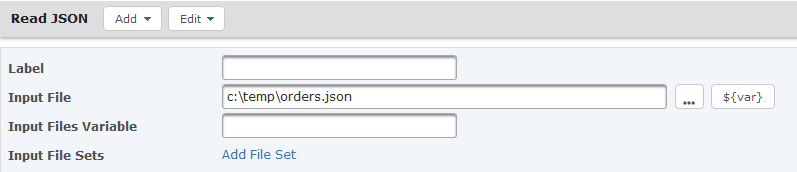
Click the Add together push button and select RowSet.

On the RowSet element, specify a value for the Variable Name attribute:
- Variable Name – The name of the variable which will incorporate the parsed data. The RowSet variable volition be used to store order information.
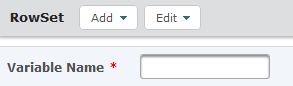
Click the Add push button and select Cavalcade.
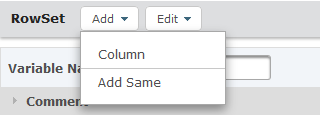
On the Column element, specify values for the post-obit attributes:
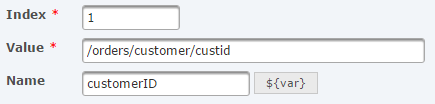
- Index – The index of the column in the output RowSet. The outset column starts with index 1.
- Value – The path to the field from which this column should draw data. To retrieve information from a field, the path should exist defined like "/Object/Array/Field". For example, to remember the social club number from the example above, use "/orders/orderno". To retrieve the customer ID, utilize "/orders/customer/custid".

Repeat the previous two steps to add additional columns for the remaining gild information.
Create a second RowSet variable to store the customer information from the JSON file.

Select the Read JSON chore from the Projection Outline and then click the Add button and select Add together RowSet to add together another RowSet variable. On the RowSet chemical element, specify a value for the Variable Proper noun attribute.
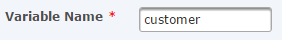
Click the Add button and select Cavalcade. On the Column element, specify values for the Index and Value attributes.
Click the Add push in the sub-card and select Add Same. Echo the last ii steps to add additional columns and elements from the JSON file.
The post-obit image illustrates the Projection Outline for the Read JSON task, which contains ii RowSet variables for columns and elements read from the JSON file:

Instance Output
To translate the data gathered from the Read JSON task into a database, expand the Database folder in the Component Library, and so drag the SQL task to the Project Outline.

On the SQL task, specify values for the following attributes:
- Database Server - Select a pre-configured database server from the drop-down listing.
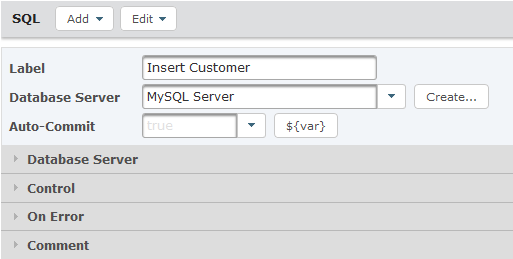
Click the Add button to Add a Query to the SQL task.
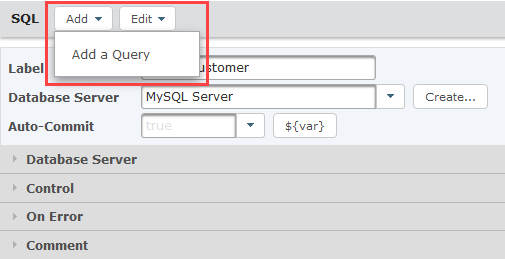
Type in your SQL Insert Statement on the folio. In this case, the table proper name is 'orders', and four placeholder '?' are used for the Indexes referenced in the 'orders' RowSet.
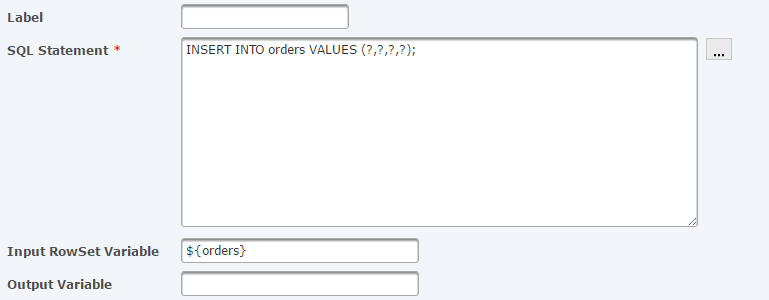
Specify the RowSet variable name '${orders}' into the Input RowSet Variable field. The specified SQL Argument will exist executed one time per each row in this RowSet.
To insert the information contained in the ${client} RowSet variable into a database, add a second query past clicking the Add together push button and Add Aforementioned. Because the ${customer} RowSet variable contains seven indexes, seven placeholder '?' are used.

The following paradigm illustrates the final Projection Outline.
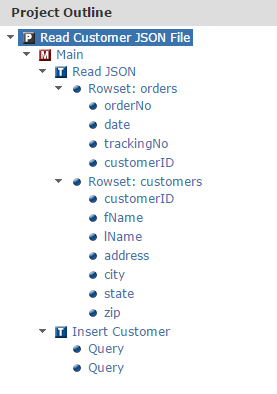
When executed, the project volition read the information from the JSON file and load that data into RowSet variables using the Read JSON chore. Those RowSets are and so used to insert the data into 2 split up database tables using the SQL task.
Are you trying to convert JSON data to other information formats? First a free trial of GoAnywhere MFT and meet how our automation tools tin can salve you time and money.
Still have questions? Browse our forum, post a question, or live chat with a technician now!
Source: https://www.goanywhere.com/managed-file-transfer/more/tutorials/parse-json-data-into-database
0 Response to "How to Read a Json From File and Put It in Mysql Java"
Post a Comment